No products in the cart.
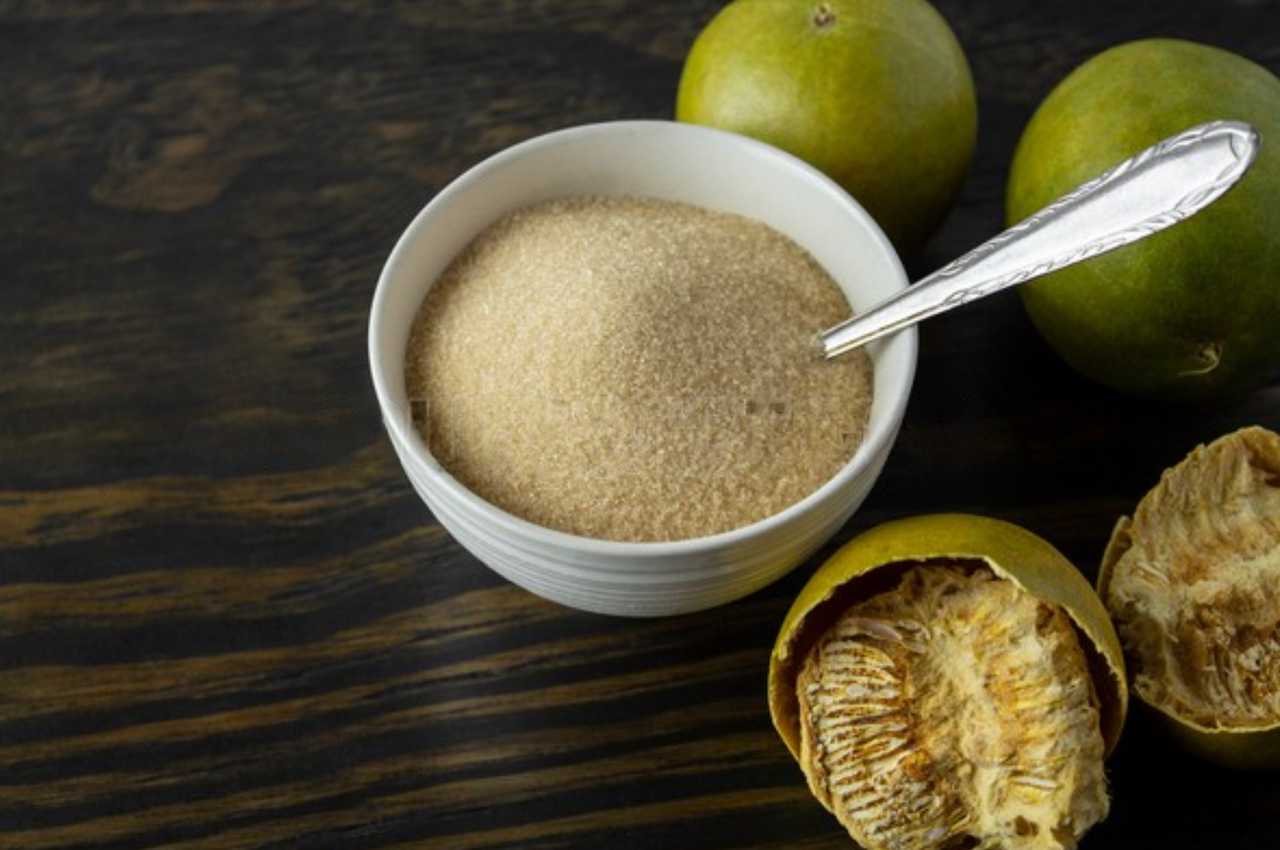
Return To Shop500g Monk Fruit is a natural sugar substitute from Luo Han Guo fruit
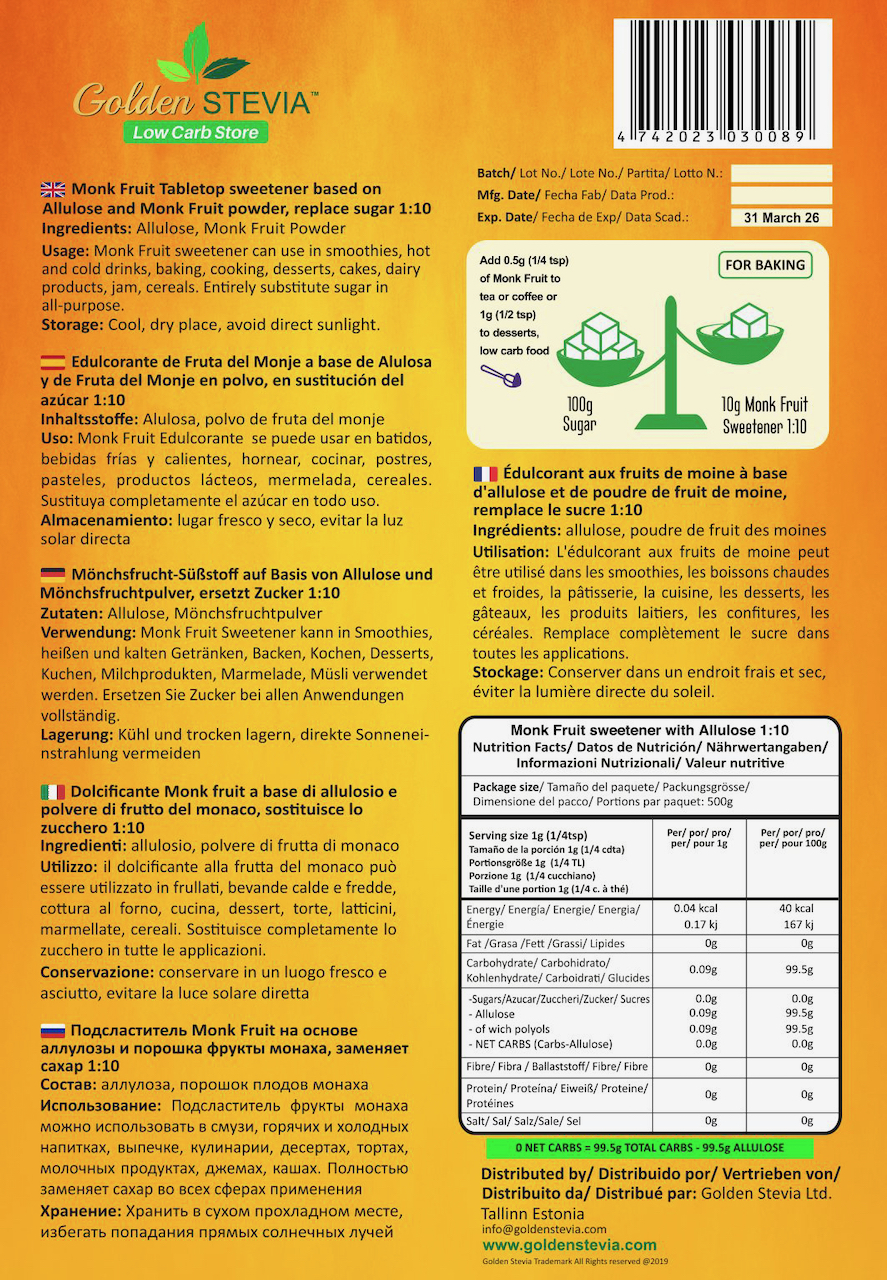
Monk Fruit with Allulose 500g 1:10 = 5 kg of sugar
Serving size 1 g (1/4 teaspoon), 1 teaspoon = 4 g
¼ teaspoon (tsp) 1 g monk fruit 1:10 = 5 teaspoons 10 g (tsp)
- Diabetes friendly
- Keto diet friendly, Low Carb #Ketodiet #lchf
- Gluten free
- Sugar free
- GMO free
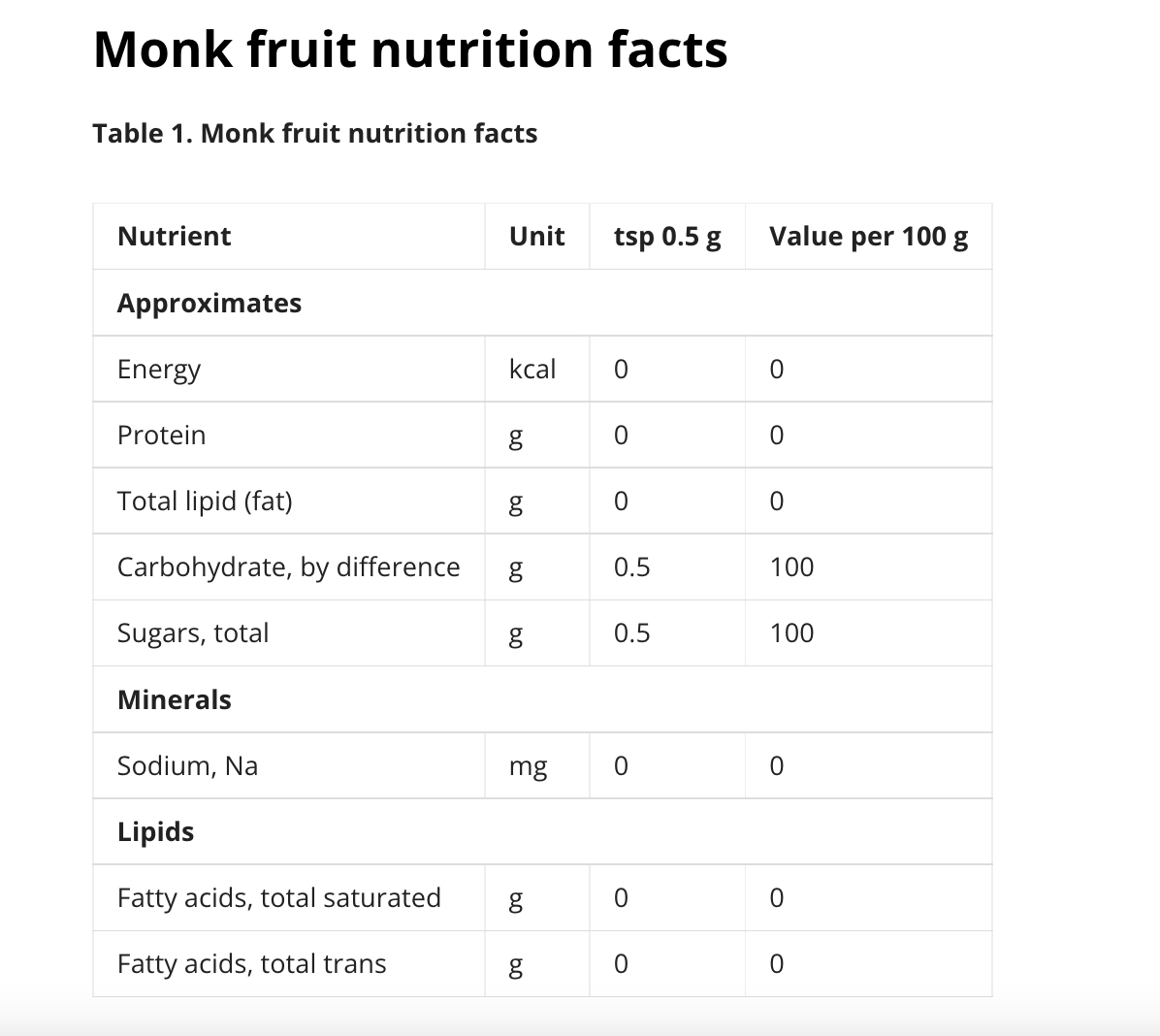
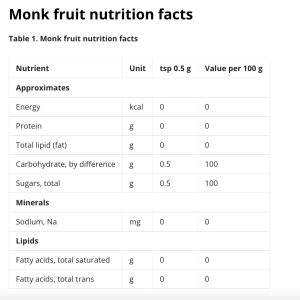
Zero carbohydrates per serving 1 g
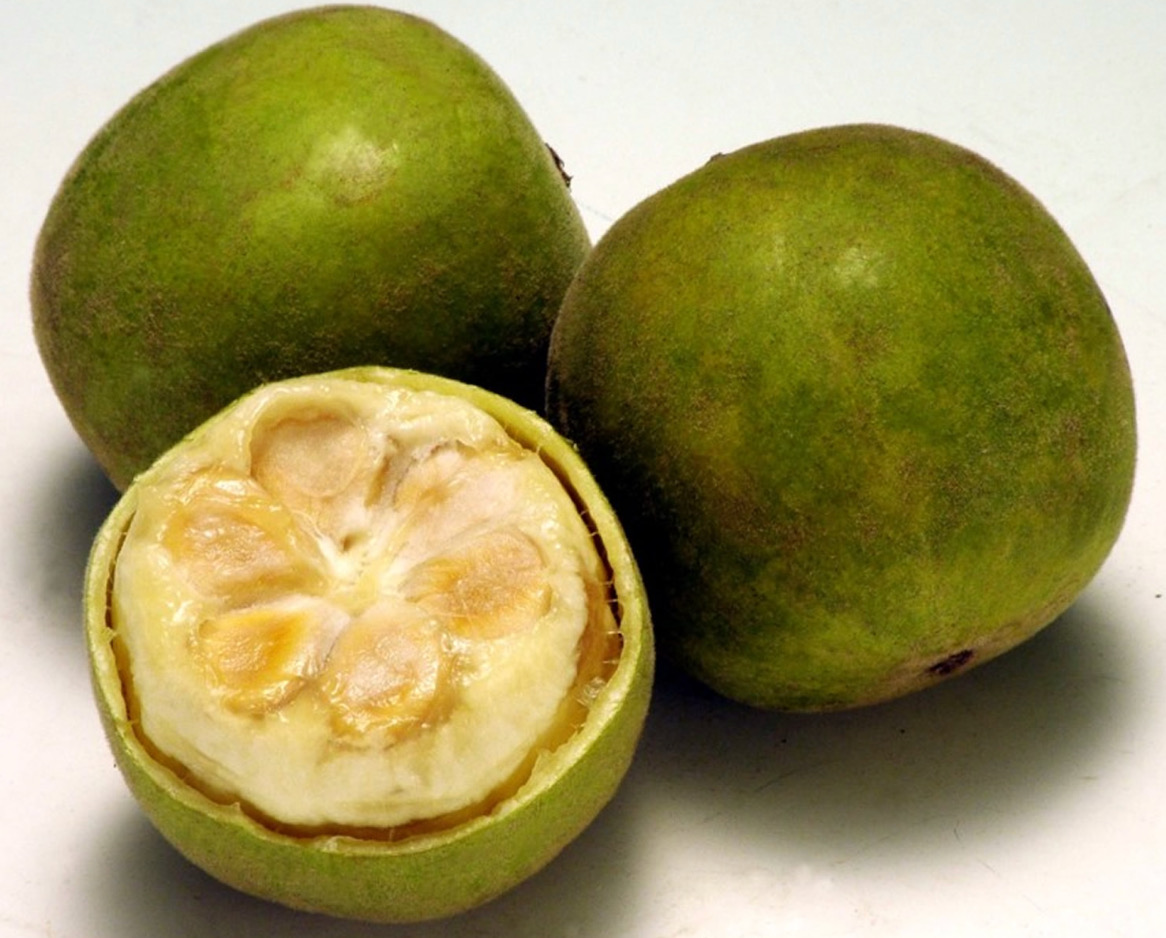
Monk fruit sugar substitute or Luo Han Guo fruit, a healthy “magic” sugar substitute. He is from southern China. The plant is grown for its fruit extract – called mogrosides – which produces a sweet taste 250 times stronger than sucrose.
- Does not increase blood sugar
- In the same way, you use very little like Golden Stevia sweetener!
- Usage 1 g per serving!
- Takes little and lasts a long time!
- The taste is fruity sugar, there is no aftertaste specific to stevia.
- Healthy and rich in minerals.
What is Monk Fruit Sugar Substitute?
Why is Monk Fruit good?
How to use Monk Fruit Sugar Substitute
Why is Monk Fruit useful?
Which is better Monk Fruit vs Stevia?
Where to find Monk Fruit recipes
Where to buy Monk Fruit sugar substitute?
What does Monk Fruit contain?
What are Sugar Alcohols (Polyols)?
More and more people give up sugar every day and look for different alternative sweeteners, sugar substitutes to make delicious desserts to add to their coffee or tea.
Monk Fruit and Stevia sugar substitutes are among the most popular. Golden Stevia brings you various healthy sugar substitute options and teaches you how to use sugar substitutes. We have developed Monk Fruit and Stevia sugar substitutes that are 10-12 times sweeter than sugar and you use very little of them, 1 gram per serving. This makes them a condiment, not a filler.
What is Monk Fruit sugar substitute or Monk Fruit or Luo Han Guo?
Monk Fruit sweetener is a natural zero calorie sweetener. It is high in unique antioxidants called mogrosides, which make it 100-250 times sweeter than regular sugar.
- Suitable for diabetics
- Does not increase blood sugar
- With good taste
- Easy to use
- Healthy
- No additives
- 0 carbs, 0 kcal, 0 GI
- Consistency of regular powder sugar
Siraitia grosvenorii, also known as monk’s tree or luo han guo, is a perennial vine in the cucurbitaceae family. He is from southern China. The plant is grown for its fruit extract, called mogrosides, which produces a sweet tooth 250 times stronger than sucrose.
The sweetener from Monk Fruit is extracted from monk fruit.
Monk Fruit VS Stevia
Monk Fruit and Stevia both come from plants. People use products made from extracts to sweeten foods and drinks. These products contain very few, if any, calories.
Advantages of Monk Fruit
Monk Fruit sweetener has several advantages over sugar:
Zero calories. Monk Fruit extract contains no calories, which is beneficial for people following a Keto, LCHF or other Low Carb diet or nutrition.
Zero carbs. The extract also does not contain carbohydrates, which can make it ideal for those following a Low Carb or Keto diet, as well as diabetics.
Zero sugar. Pure Monk Fruit extract does not contain sugar, which means that its consumption does not affect blood sugar levels.
There are no harmful side effects. A reliable source from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) states that Monk Fruit sweeteners are generally considered safe. There appears to be no evidence that Monk Fruit sweeteners cause any harmful side effects.
Available in several forms. Monk Fruit sweeteners are marketed as granules, powders and liquids. Some products can be easy to carry around and use throughout the day.
Monk Fruit sweeteners may also have some health benefits:
Antioxidants. Some animal studies indicate that mogrosides extracted from Monk Fruit may have strong antioxidant properties. Further research is needed to understand the effect on humans.
Diabetes. Animal studies also show that mogrosides play a role in controlling blood sugar levels. The results of another study show that mogroside extracts may help prevent diabetes complications. However, scientists have yet to study these effects in humans.
minuses of Monk Fruit with allulose
Availability and cost. Monk Fruit are difficult to grow and expensive to export, meaning they are not as widely available as other sweeteners and can be expensive.
Taste. Monk Fruit sweeteners taste different from regular table sugar and some find the taste unusual or unpleasant. Sweeteners can also leave an aftertaste.
Other ingredients. Some manufacturers balance the taste of Monk Fruit by mixing it with other sugars such as maltodextrin or dextrose. This can change the nutritional profile of the sweetener and make it unsafe or undesirable for some people.
A choice between Monk Fruit and Stevia
Monk Fruit and Stevia have very similar properties. For many, the choice between the two simply comes down to personal preference. A person may want to try both and see which one they prefer.
| Weight | 0,5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 12 × 5 × 24 cm |
| Ingredients: | Allulose, Monk Fruit Powder |
| Usage: | Monk Fruit sweetener can use in smoothies, hot and cold drinks, baking, cooking, desserts, cakes, dairy products, jam, cereals. Entirely substitute sugar in all-purpose. |